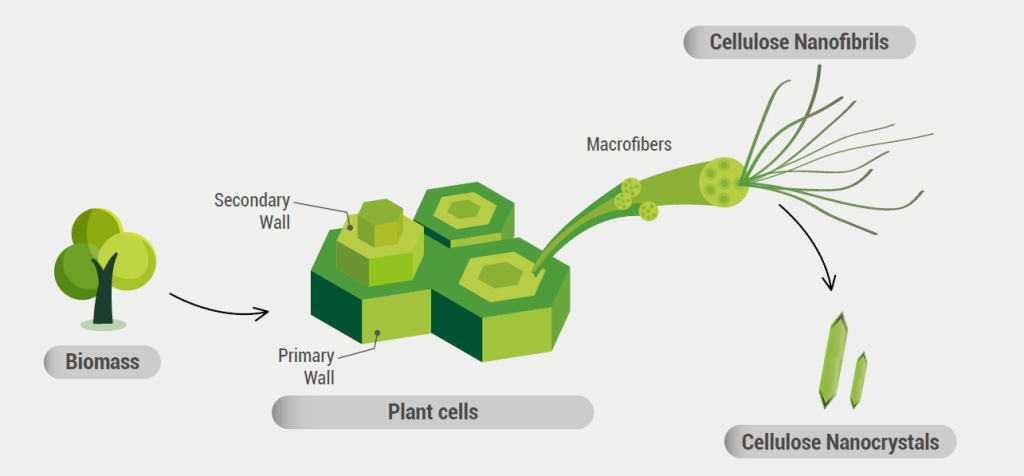
Cellulose products
SCYCLE Advanced Cellulose Technology Solutions
MicroFibrillated Cellulose
Microfibrillated cellulose
MFC is a nanomaterial obtained by microfibrillation of cellulose fibres through mechanical treatment, with high aspect ratio, high specific surface area and excellent mechanical properties.

nanoscale
Diameter 10-50 nm, L/D ratio up to 1000
high strength
Excellent mechanical strength and toughness
Good dispersion
Forms a stable suspension in water
renewable (resource)
Derived from natural cellulose, environmentally sustainable
Areas of application
Cellulose Nanofiber
Nanocellulose fibres
CNF is a cellulose fibre with a nanoscale diameter, which maintains the crystalline structure of cellulose and has a very high specific surface area and excellent mechanical properties.
microfibre
Diameter 2-20 nm, length up to micron scale
high barrier
Excellent gas and liquid barrier properties
thermal stability
Good thermal and dimensional stability
thixotropic
Unique rheological properties
Areas of application

Cellulose Nanocrystal
Cellulose nanocrystals
CNC is a highly crystalline nanocellulose obtained by acid hydrolysis to remove the amorphous regions, with excellent mechanical properties and unique optical properties.

High crystallinity
Crystallinity up to 90% or more
optical property
With birefringence and liquid crystal phase behaviour
surface charge
Negatively charged surface, easily chemically modified
high modulus
Young's modulus up to 150 GPa
Areas of application
technical specification
| Technical indicators | Numerical range | unit (of measure) | Application Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fibre diameter | 5-20 | nm | Microfibre, excellent dispersion |
| lengths | 100-2000 | μm | High L/D ratio for significant enhancement |
| tensile strength | 7.5-7.7 | GPa | High strength, alternative to traditional materials |
| transparency | 85-95 | % | Highly transparent for optical applications |
| biodegradability | 100 | % | Fully biodegradable and environmentally friendly |
CNF vs CNC technology
Having a fibre form with an aspect ratio of 1/100 or greater
Manufacturing process: Mechanical methods are used so that the fibres can be kept in their original state.
Characteristics: Maintains intact fibre structure with excellent reinforcing effect.
Has a crystal form with an aspect ratio of 1/50 or less
Manufacturing process: Manufactured by acid hydrolysis reaction (treatment with sulphuric acid, etc.)
Characteristics: High purity in the crystalline state region with unique optical properties
The reason for the difference in morphology between CNF and CNC is the manufacturing method. Since CNF is manufactured mechanically, the fibres are able to remain in their original form as a whole; whereas CNC is manufactured by acid hydrolysis reaction, and its crystal form is such that the amorphous regions are dissolved by strong acids, leaving only the crystalline regions. Although different scholars have different criteria for distinguishing between CNF and CNC, they are generally distinguished by shape and aspect ratio (diameter/length).
Bacterial Nanocellulose
Bacterial nanocellulose
BNC is a pure nanocellulose produced by bacterial fermentation with a unique 3D network structure and excellent biocompatibility.
biosynthesis
Produced by bacterial fermentation, very high purity
biocompatibility
Excellent biocompatibility and non-toxicity
3D network structure
Unique 3D nanofibre network
High water holding capacity
Absorbs 99% of water by its own weight
Areas of application